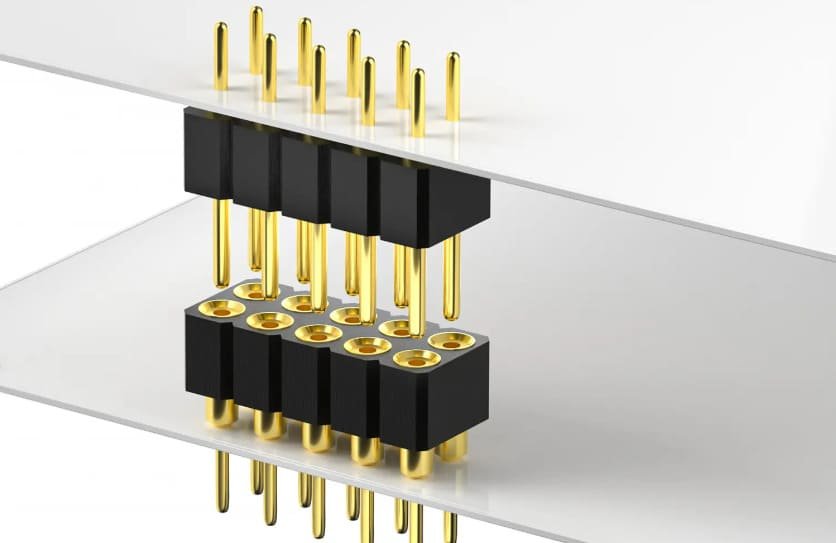
Connector pins serve as the vital links in countless electronic and mechanical systems, ensuring reliable power transmission and signal integrity across industries. When manufactured through CNC machining processes, these components achieve exceptional dimensional accuracy and consistency that alternative methods simply cannot match. This precision becomes particularly crucial in high-stakes applications where connector failure could lead to system-wide malfunctions.
The Critical Role of Connector Pins in Modern Industries
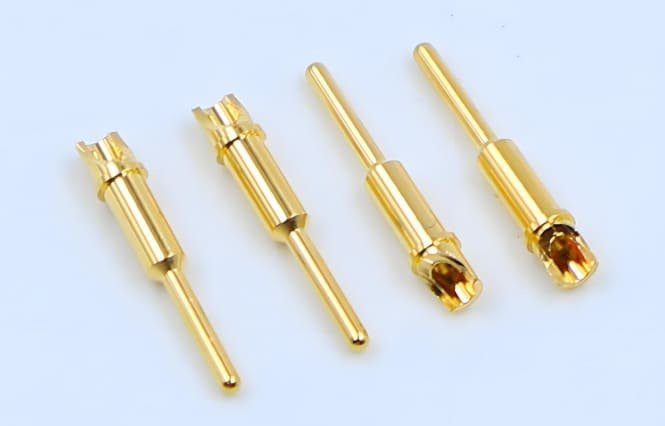

Connector pins may be small in size, but their impact on system functionality is immense. These precision components establish the electrical and mechanical connections that power everything from consumer electronics to aerospace systems. The reliability of these connections directly affects product performance, safety, and longevity.
Key Industries Relying on Precision Connector Pins
- Electronics manufacturing (circuit boards, sensors, displays)
- Automotive systems (ECUs, sensors, battery management)
- Aerospace and defense (navigation systems, communication equipment)
- Medical devices (patient monitoring, diagnostic equipment)
- Industrial automation (control systems, robotics)
- Telecommunications (network infrastructure, data centers)
In these demanding environments, connector pins must maintain consistent electrical conductivity while withstanding mechanical stress, temperature fluctuations, vibration, and potential corrosion. The precision achieved through CNC machining ensures these critical requirements are met consistently.
Advantages of CNC Machining for Connector Pins

CNC machining offers significant advantages over alternative manufacturing methods when producing connector pins. The computer-controlled precision of these systems delivers consistent quality that’s essential for components where tolerances are measured in micrometers.
Advantages of CNC Machining for Connector Pins
- Exceptional Precision – Tolerances as tight as ±0.01mm for perfect fit and function
- Consistent Quality – Batch-to-batch uniformity ensures reliable performance
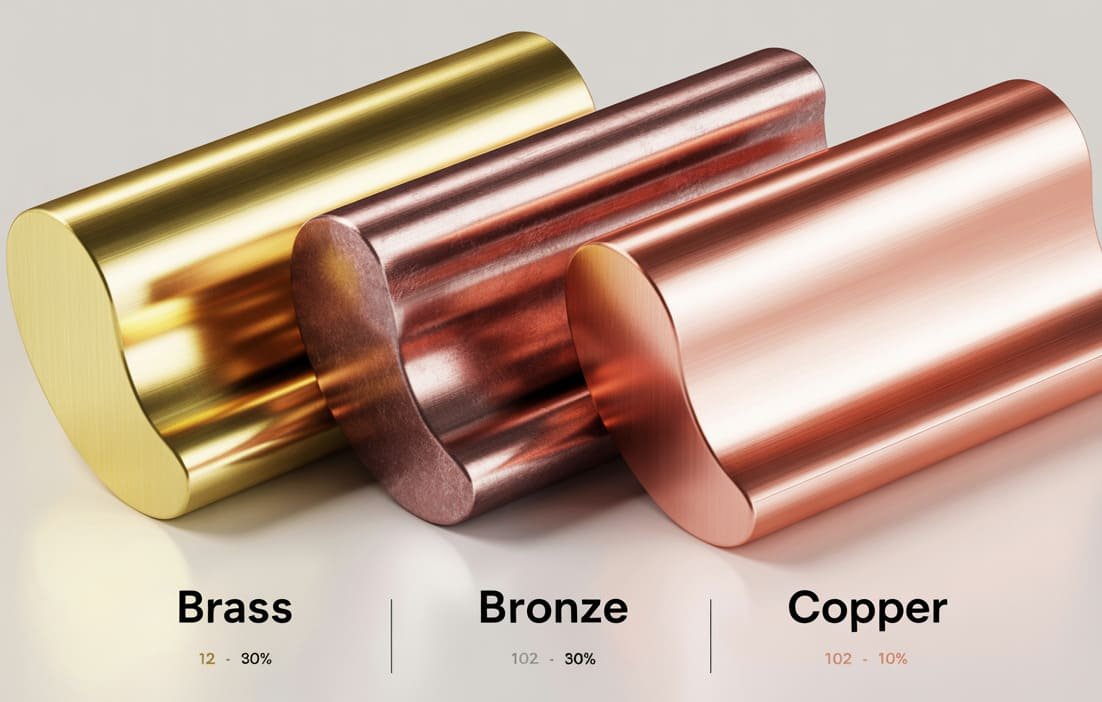
- Material Versatility – Compatible with conductive metals like brass, copper, and stainless steel
- Complex Geometries – Ability to create intricate features like threads and grooves
- Surface Finish Control – Smooth surfaces for better electrical contact
- Rapid Prototyping – Quick turnaround for design validation
- Scalability – Efficient for both small and large production runs
Limitations to Consider
- Higher Unit Cost – More expensive than stamping for very high volumes
- Material Waste – Subtractive process generates more scrap
- Size Limitations – Very small features (sub-0.1mm) can be challenging
- Setup Time – Initial programming and tooling setup required
Materials for CNC Machined Connector Pins
The material selection for connector pins significantly impacts their performance characteristics, including conductivity, corrosion resistance, and mechanical strength. CNC machining accommodates a wide range of metals suitable for various connector applications.
| Material | Conductivity | Corrosion Resistance | Strength | Cost | Best Applications |
| Brass (C36000) | High | Good | Medium | Low-Medium | General electronics, consumer products |
| Phosphor Bronze | High | Excellent | High | Medium | Spring contacts, marine applications |
| Beryllium Copper | Very High | Excellent | Very High | High | Aerospace, military, high-reliability systems |
| Stainless Steel 303/304 | Low | Excellent | High | Medium | Harsh environments, structural support |
| Aluminum (6061) | Medium | Good | Medium | Low | Weight-sensitive applications |
Common Plating Options for Enhanced Performance
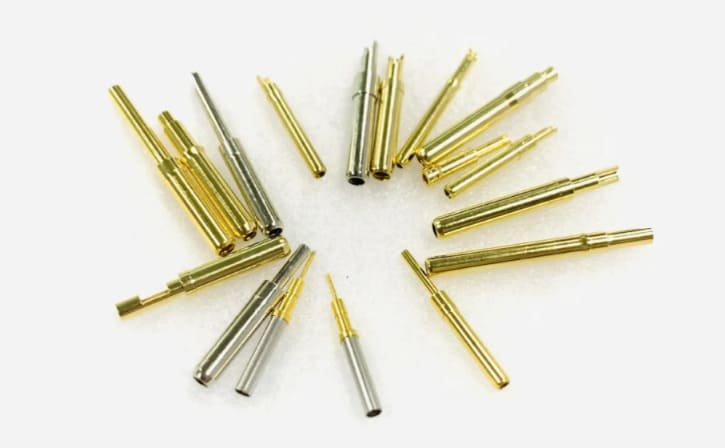

Surface plating enhances connector pin performance by improving conductivity, wear resistance, and corrosion protection. The right plating can significantly extend connector lifespan in challenging environments.
Gold Plating
Provides excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. Thickness ranges from 0.1μm (flash) to 3μm (hard gold). Ideal for low-voltage, high-reliability applications.
Nickel Plating
Offers good wear resistance and serves as an excellent base layer. Typical thickness: 1-5μm. Often used as an undercoat for gold to reduce costs.
Tin Plating
Cost-effective solution with good solderability. Thickness: 2-8μm. Commonly used in consumer electronics and non-critical applications.
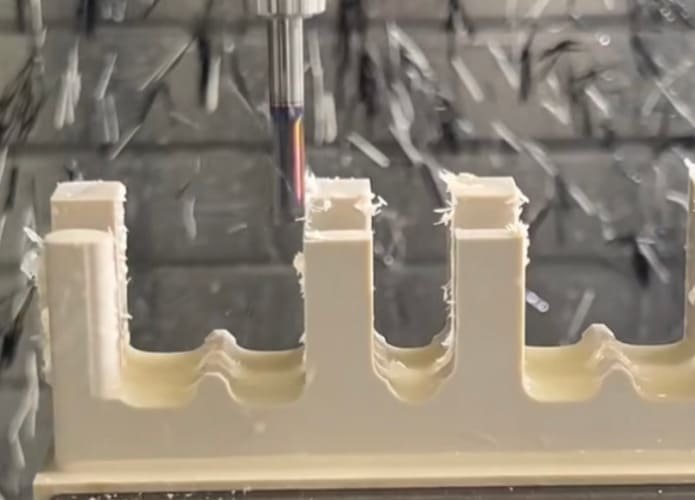
CNC Machining Processes for Connector Pins
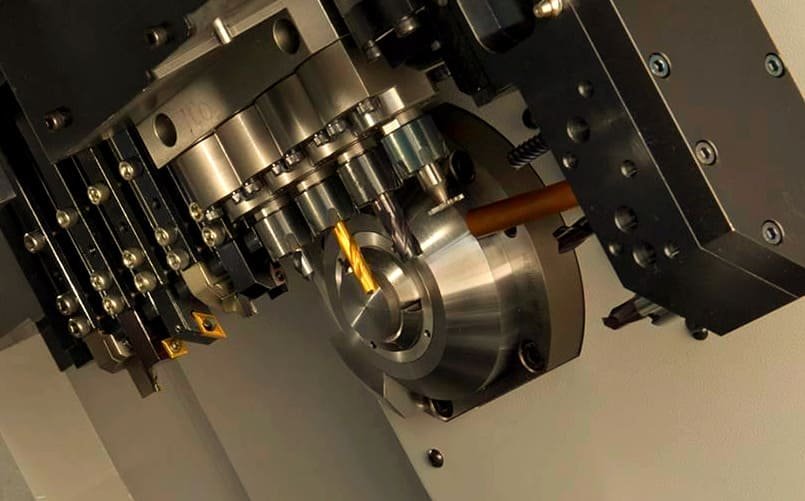

The selection of the appropriate process depends on pin geometry, production volume, and precision requirements.
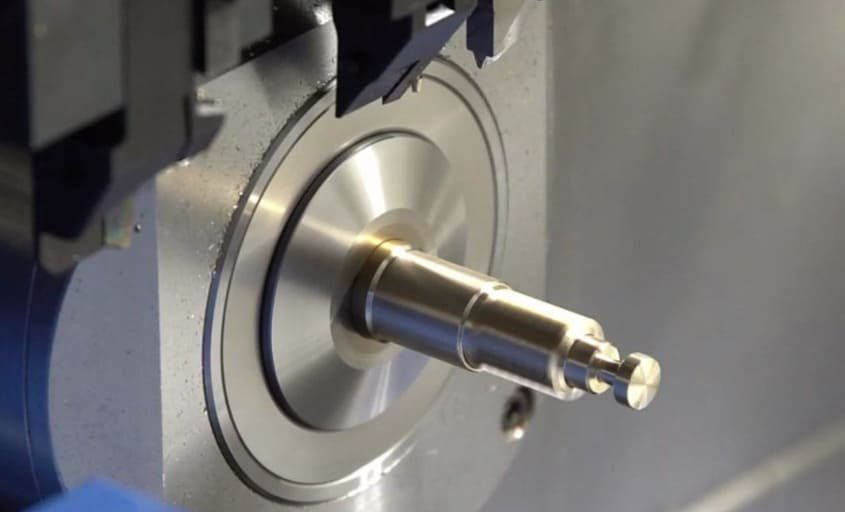
Swiss-Type CNC Turning
Swiss-type lathes excel at producing small, precise connector pins with tight tolerances. These machines support the workpiece along its entire length during machining, minimizing deflection and enabling the production of long, slender pins with exceptional straightness and concentricity.
Key Advantages:
- Superior precision for small diameter pins (0.5mm-20mm)
- Excellent surface finish requiring minimal post-processing
- Ability to machine complex features in a single setup
- High production efficiency for medium to large volumes
CNC Milling for Complex Features
While turning is the primary process for creating the cylindrical body of connector pins, CNC milling is often employed to add complex features such as flats, slots, and non-round geometries. Multi-axis milling centers can produce intricate connector pin designs that would be impossible with turning alone.
Applications:
- Creating D-shaped sections for anti-rotation features
- Milling slots and grooves for retention mechanisms
- Adding complex surface features for specialized connections
- Secondary operations on turned connector blanks
Automated Production Systems
For high-volume connector pin production, automated CNC machining cells combine multiple processes including turning, milling, threading, and inspection. These systems maximize efficiency while maintaining the precision required for connector applications.
Design Considerations for CNC Machined Connector Pins
Effective connector pin design balances electrical performance, mechanical integrity, and manufacturability.
Dimensional Tolerances
Typical connector pin tolerances range from ±0.01mm to ±0.05mm depending on the application. Critical dimensions include pin diameter, length, and any engagement features. Tighter tolerances increase manufacturing costs but ensure proper fit and function.
Surface Finish Requirements
Surface roughness directly impacts electrical contact resistance and wear characteristics. For connector pins, Ra values between 0.2-0.8μm are typical. Smoother finishes improve conductivity but may require additional polishing operations.
Feature Geometry
Design features like chamfers, radii, and tapers facilitate easier insertion and improve durability. Avoid sharp corners that can cause stress concentration. Minimum feature size is typically limited to 0.1-0.2mm for most CNC processes.
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) Guidelines
Following these DFM principles helps optimize connector pin designs for efficient CNC machining while maintaining functional requirements:
- Standardize dimensions where possible to reduce setup changes and tooling requirements
- Minimize length-to-diameter ratios (ideally below 15:1) to reduce deflection during machining
- Specify appropriate tolerances based on functional needs rather than arbitrarily tight requirements
- Consider tool access for all features, especially internal geometries
- Design for minimal setups to reduce handling and improve consistency
Quality Control for CNC Machined Connector Pins
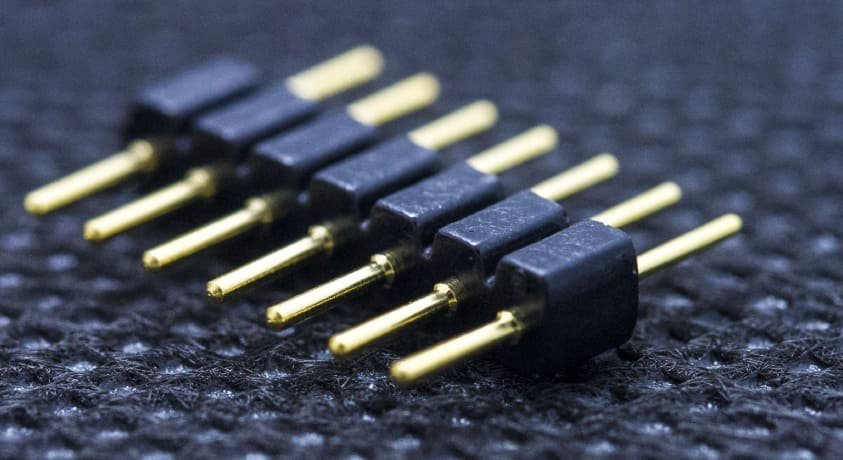
Rigorous quality control procedures ensure that connector pins meet all specified requirements. From dimensional inspection to electrical testing, these processes verify that each pin will perform reliably in its intended application.
Dimensional Verification
- Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM) for high-precision 3D measurement
- Optical comparators for profile inspection
- Micrometers and calipers for quick dimensional checks
- Thread gages for threaded connector pins
Functional Testing
- Insertion and extraction force testing
- Electrical conductivity measurement
- Contact resistance testing
- Durability testing (insertion cycles)
Surface Quality Assessment
- Profilometers for surface roughness measurement
- Visual inspection under magnification
- Scanning electron microscopy for detailed surface analysis
Material Verification
- X-ray fluorescence (XRF) for material composition
- Hardness testing
- Plating thickness measurement
- Adhesion testing for plated surfaces
Quality Standards and Certifications
Connector pin manufacturers typically adhere to industry standards that ensure consistent quality and compatibility:
| Standard/Certification | Description | Relevance to Connector Pins |
| ISO 9001 | Quality management system | Ensures consistent manufacturing processes and quality control |
| ISO 13485 | Medical device quality management | Critical for medical device connector applications |
| AS9100 | Aerospace quality management | Required for aerospace and defense connector pins |
| IATF 16949 | Automotive quality management | Essential for automotive electrical connector pins |
| RoHS/REACH | Hazardous substance restrictions | Ensures environmental compliance of materials and plating |
Applications of CNC Machined Connector Pins
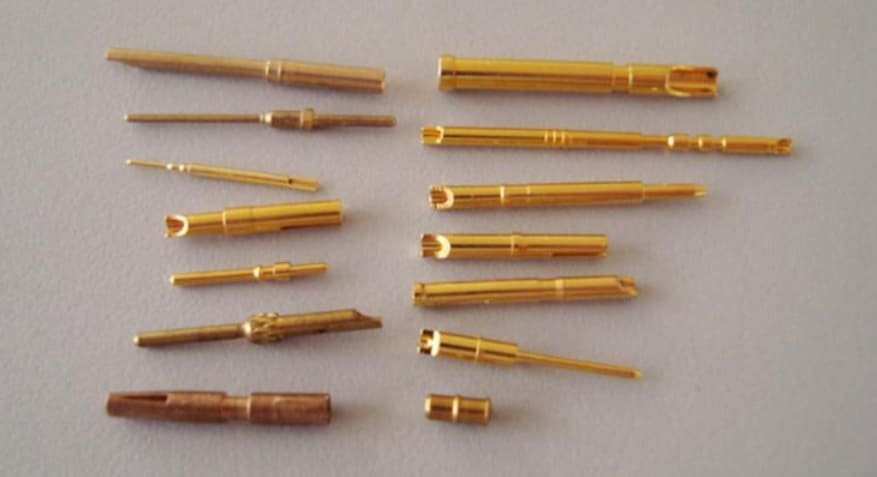

The precision and reliability of CNC machined connector pins make them ideal for numerous applications across diverse industries. Each application presents unique requirements that influence connector pin design and manufacturing specifications.
Electronics and Telecommunications
- PCB header pins and sockets
- RF connector contacts
- High-density backplane connectors
- Test probe pins for circuit testing
- Power distribution connectors
Automotive Applications
- Engine control unit connectors
- Sensor interface pins
- Battery management system contacts
- Charging port connectors for EVs
- Airbag system connectors
Aerospace and Defense
- MIL-spec circular connectors
- Avionics system interconnects
- Satellite communication equipment
- Radar system connectors
- Flight control system interfaces
Medical Devices
- Patient monitoring equipment
- Surgical instrument connectors
- Implantable device feedthroughs
- Diagnostic equipment interfaces
- Medical imaging system connectors
Industrial Automation
- Robotic system interconnects
- Industrial sensor connectors
- PLC interface connectors
- Motor control connections
- Factory automation equipment
Energy and Power
- High-voltage power distribution
- Solar inverter connections
- Battery storage system interfaces
- Wind turbine control connectors
- Transformer monitoring equipment
Future Trends in Connector Pin Manufacturing
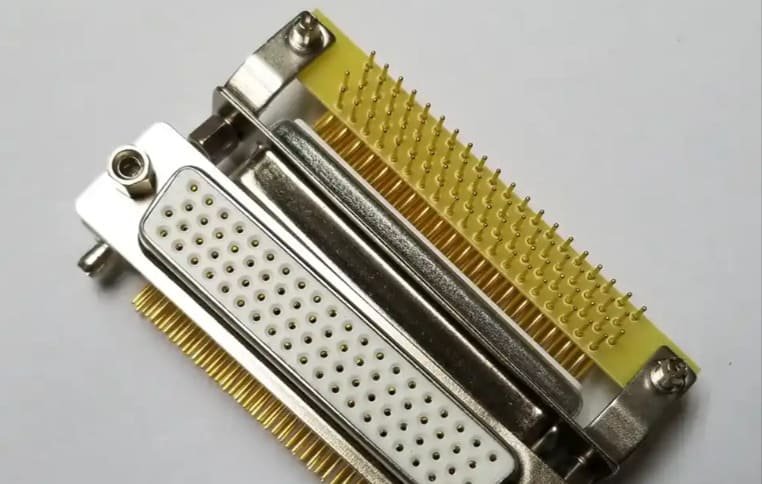

The connector pin industry continues to evolve in response to changing technological demands and manufacturing capabilities. Several key trends are shaping the future of CNC machined connector pins.
Miniaturization
As electronic devices become smaller and more compact, connector pins must follow suit. Advanced CNC machining techniques are pushing the boundaries of miniaturization, with some manufacturers now capable of producing pins with diameters as small as 0.3mm while maintaining tight tolerances.
Advanced Materials
New alloys and composite materials are being developed to meet demanding requirements for conductivity, strength, and environmental resistance. These materials often present unique machining challenges that require specialized CNC processes and tooling.
Integrated Manufacturing
The trend toward fully automated production cells combines CNC machining with in-line inspection, cleaning, and plating processes. These integrated systems improve efficiency, reduce handling damage, and ensure consistent quality.
Sustainability Initiatives
Environmental considerations are driving improvements in machining efficiency, material utilization, and waste reduction. Modern CNC processes aim to minimize material waste through optimized tool paths and near-net-shape starting materials.
Digital Manufacturing
Industry 4.0 principles are transforming connector pin production through digital twins, predictive maintenance, and real-time quality monitoring. These technologies enable unprecedented levels of process control and traceability.
Conclusion
CNC machining remains the gold standard for producing high-precision connector pins that meet the demanding requirements of modern electronic and mechanical systems. The exceptional dimensional accuracy, material versatility, and surface quality achievable through CNC processes ensure reliable electrical connections and mechanical integrity in critical applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the typical tolerances achievable for CNC machined connector pins?
Standard tolerances for CNC machined connector pins typically range from ±0.01mm to ±0.05mm depending on the feature and dimension. Critical dimensions like pin diameter often require tighter tolerances (±0.01mm) to ensure proper fit and electrical contact, while less critical features may have more relaxed tolerances. For extremely precise applications, tolerances as tight as ±0.005mm can be achieved with specialized equipment and processes.
How do I choose between brass and stainless steel for connector pins?
The choice between brass and stainless steel depends on your application requirements. Brass offers excellent electrical conductivity (approximately 28% IACS) and good machinability, making it ideal for standard electrical connections in controlled environments. Stainless steel provides superior corrosion resistance and mechanical strength but with lower conductivity (approximately 3-5% IACS), making it better suited for harsh environments or applications where mechanical properties are prioritized over electrical performance.
What surface finishes are available for CNC machined connector pins?
Common surface finishes include gold plating (0.1-3μm thickness) for optimal conductivity and corrosion resistance, nickel plating (1-5μm) for wear resistance, tin plating (2-8μm) for cost-effective solderability, and silver plating for high-frequency applications. Surface roughness can be controlled through machining parameters and post-processing, with typical Ra values ranging from 0.2μm (polished) to 0.8μm (standard machined finish).