Are visible tool marks on your CNC machined parts compromising their quality and performance? As a CNC machining manufacturer, CNCPOR understands the importance of achieving high-quality surface finishes.
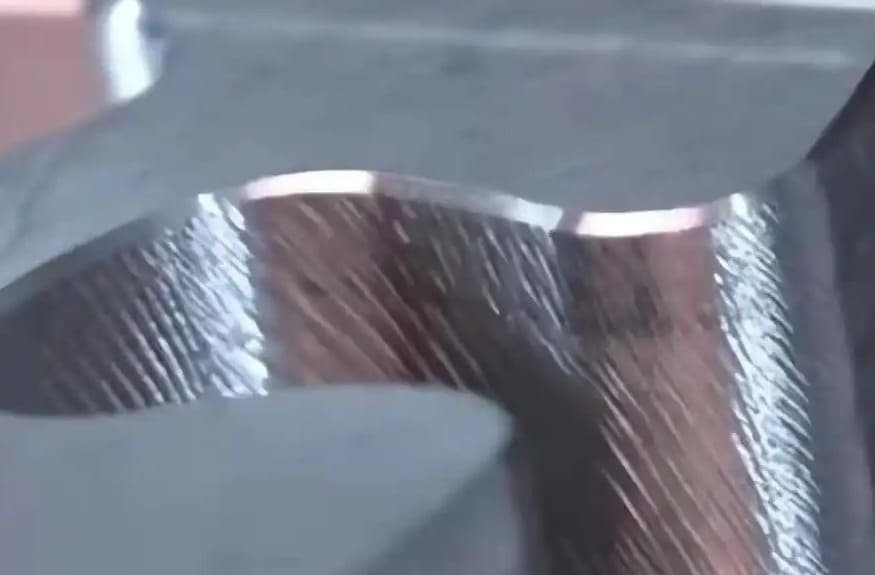
Tool marks refer to the visible lines or ridges left on a machined surface due to the interaction of the cutting tool with the workpiece. These marks can affect not only the aesthetics but also the performance and accuracy of the parts.
You might be wondering how to minimize these defects and improve overall manufacturing quality. In this article, we will explore the causes of tool marks on CNC machined parts and provide practical solutions to achieve a superior surface finish.
Understanding Tool Marks in CNC Machining
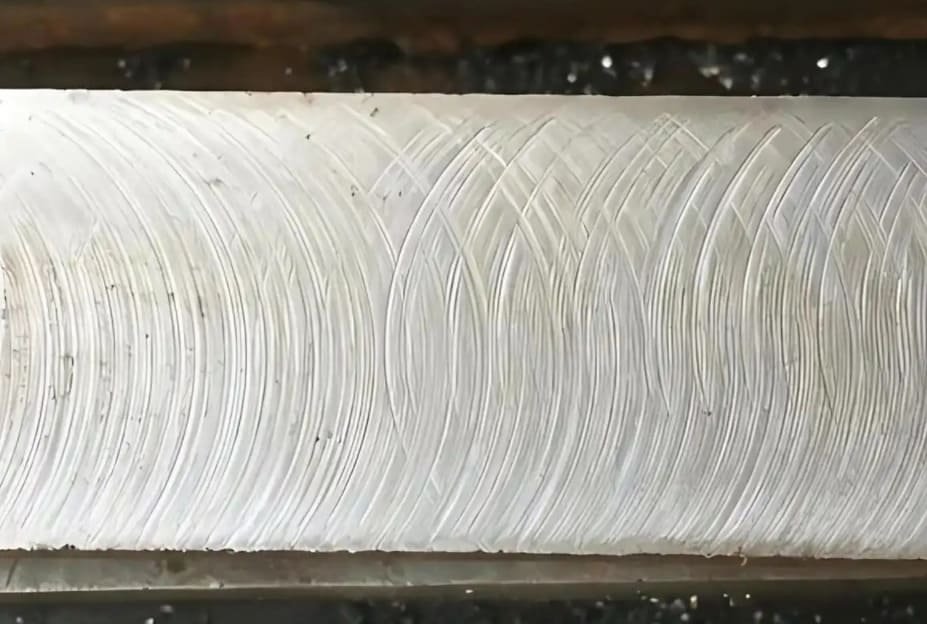

Understanding the causes and effects of tool marks is crucial for achieving high-quality surface finishes in CNC machining. Tool marks are a common issue that can arise during the machining process, and their impact on part quality and performance can be significant.
Definition and Types of Tool Marks
Tool marks can be defined as the visible lines or ridges left on a machined surface due to the cutting tool’s interaction with the workpiece. There are various types of tool marks, including those caused by improper tool selection, machine vibration, and incorrect cutting parameters. You should be aware that these marks can be categorized based on their appearance and the machining process used.
For instance, some common types of tool marks include:
- Feed marks: These are the marks left on the surface due to the tool’s feed rate.
- Vibration marks: These occur due to machine vibration during the machining process.
- Tear-out marks: These are caused by the tearing of the workpiece material during machining.
Impact on Part Quality and Performance
Tool marks can significantly affect the quality and performance of the machined part. They can lead to increased surface roughness, which may compromise the part’s functionality, especially in applications where surface finish is critical. You need to consider how tool marks might impact your specific application, whether it’s in terms of wear resistance, fatigue life, or aesthetic appeal.
Moreover, tool marks can also influence the assembly and mating of parts. For example, excessive tool marks on a mating surface can lead to improper fitment or increased wear during operation. Therefore, understanding and controlling tool marks is essential for ensuring the overall quality of the machined parts.
How Tool Marks Affect Surface Finish Requirements
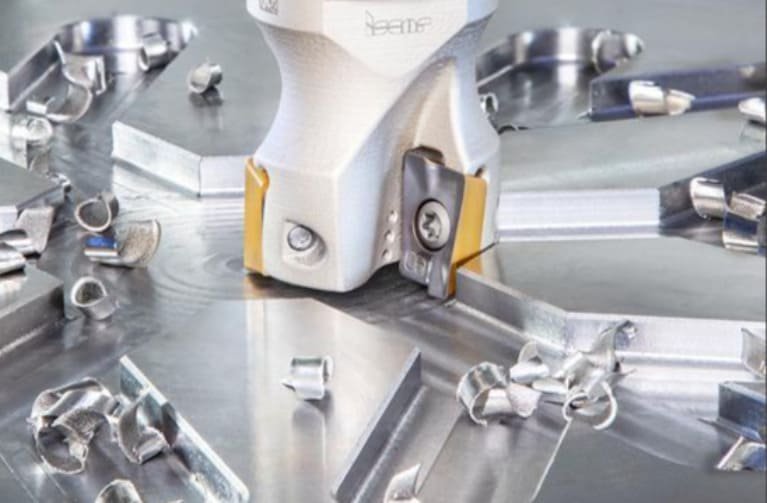

Surface finish requirements are a critical aspect of CNC machining, and tool marks play a significant role in determining whether these requirements are met. The presence and characteristics of tool marks can directly affect the surface roughness and overall finish of the machined part. You should be aware that different machining processes and tools can produce varying levels of surface finish, and tool marks are a key factor in this regard.
To achieve the desired surface finish, it’s essential to understand how tool marks are generated and how they can be controlled or minimized. This involves optimizing cutting parameters, selecting the appropriate tooling, and ensuring that the machine is properly maintained and calibrated.
Primary Causes of Tool Marks on CNC Machined Parts
CNC machined parts often exhibit tool marks due to various factors related to the machining process. Understanding these causes is crucial for optimizing the machining operation and achieving the desired surface finish.
Improper Cutting Parameters
One of the primary causes of tool marks is the use of improper cutting parameters. Cutting parameters such as feed rate, spindle speed, and depth of cut significantly impact the machining process. If these parameters are not optimized for the specific workpiece material and tooling, they can lead to tool marks. For instance, a feed rate that is too high can cause the tool to vibrate or chatter, resulting in visible marks on the machined surface.
You can avoid such issues by carefully selecting and optimizing cutting parameters based on the material being machined and the tooling used. For example, using a lower feed rate and adjusting the spindle speed can help minimize tool marks.
Tool Wear and Degradation
Tool wear and degradation are other significant factors that contribute to tool marks. As tools wear out, their geometry changes, leading to altered cutting dynamics. A worn tool can cause increased vibration, chatter, or uneven cutting, all of which result in tool marks on the machined part.
Regular tool maintenance and replacement are essential to prevent tool wear from affecting the machining process. You should monitor tool condition closely and replace tools when necessary to maintain optimal cutting performance.
Machine Vibration and Rigidity Issues
Machine vibration and rigidity issues can also lead to tool marks. If the CNC machine is not properly calibrated or if there are issues with its rigidity, it can cause the tool to vibrate excessively during machining. This vibration can result in tool marks on the workpiece.
Ensuring that the machine is well-maintained, properly calibrated, and adequately rigid is crucial. You can also use damping systems or adjust the machining process to minimize vibration.
Workpiece Material Considerations
The properties of the workpiece material play a significant role in the likelihood of tool marks. Materials that are too hard or too ductile can be challenging to machine, leading to tool marks. For example, very hard materials can cause rapid tool wear, while ductile materials might cause the tool to stick or vibrate.
Understanding the characteristics of the workpiece material allows you to adjust the machining process accordingly. This might involve selecting different tooling or adjusting cutting parameters to better suit the material being machined.
Identifying and Diagnosing Tool Mark Problems
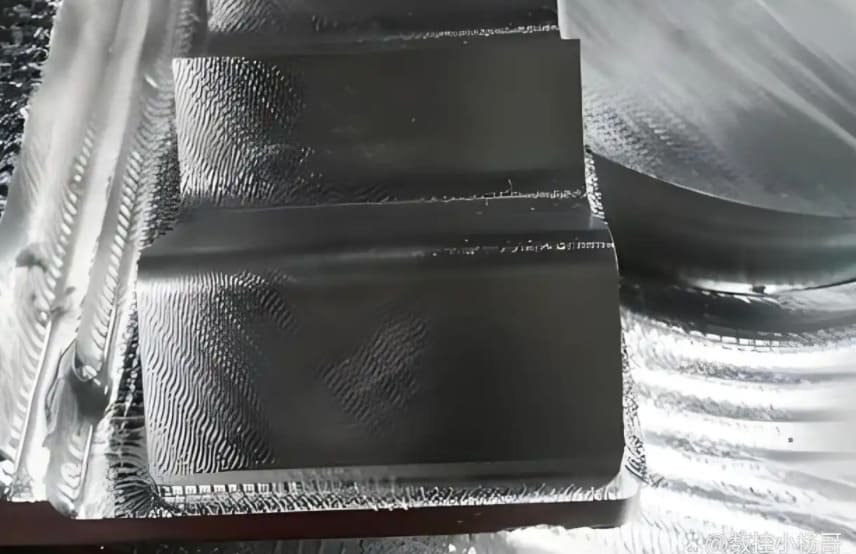

You need to employ a combination of techniques to identify and analyze tool marks, which can significantly impact the quality and functionality of the final product.
Visual Inspection Techniques
Visual inspection is a primary method for detecting tool marks on CNC machined parts. You can use various lighting techniques and angles to highlight surface defects, making it easier to identify tool marks. Careful observation is key to detecting even minor imperfections that could affect part performance.
During visual inspection, you should look for patterns or irregularities on the surface that could indicate tool wear or other issues. This method is particularly useful for identifying larger tool marks or those that are visible to the naked eye.
Surface Roughness Measurement Methods
Surface roughness measurement provides quantitative data on the surface finish of CNC machined parts, helping you to identify tool marks that may not be visible to the naked eye. You can use various instruments, such as profilometers or roughness testers, to measure surface roughness parameters like Ra, Rz, or Rq.
These measurements can be compared to specified surface finish requirements to determine if the part meets the necessary standards. By analyzing surface roughness data, you can gain insights into the condition of your cutting tools and the effectiveness of your machining processes.
Pattern Recognition in Different Types of Tool Marks
By analyzing the pattern and characteristics of tool marks, you can determine whether they are caused by tool wear, vibration, or other factors. This information is essential for taking corrective action to prevent future tool mark problems.
- Identify the type of tool mark (e.g., chatter marks, feed marks)
- Analyze the pattern and frequency of tool marks
- Correlate tool mark characteristics with machining parameters and tool condition
Using Process Monitoring Systems
Process monitoring systems can be used to detect anomalies during machining, enabling prompt corrective action to prevent tool mark problems. These systems can monitor various parameters, such as cutting forces, vibration, or spindle power, to detect deviations from normal operating conditions.
By using process monitoring systems, you can identify potential tool mark problems early, reducing the risk of part rejection or rework. This proactive approach can help you maintain consistent part quality and improve overall machining efficiency.
How to prevent and solve the tool marks that occur on CNC parts?
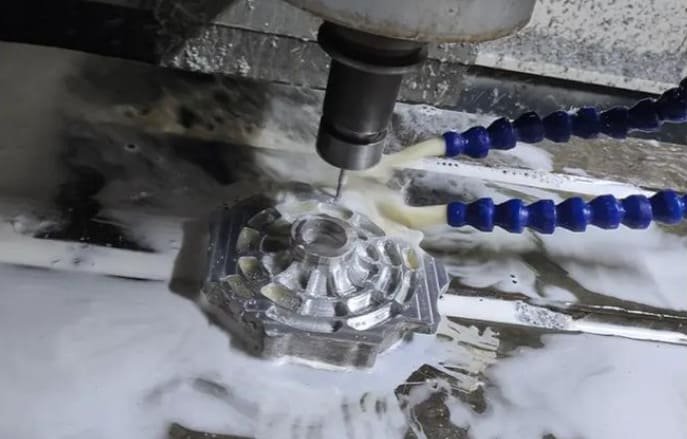

The presence of tool marks on CNC machined parts can be mitigated by optimizing various aspects of the machining process. You can achieve a smoother surface finish by addressing the root causes of tool marks and implementing effective solutions.
1. Optimizing Cutting Parameters
One crucial step in minimizing tool marks is optimizing cutting parameters. This includes adjusting feed rates and spindle speeds to suit the specific material being machined. For instance, using the correct feed rate can help reduce the likelihood of tool marks, while an optimal spindle speed can improve the surface finish.
- Reduce feed rates for finer surface finishes
- Adjust spindle speeds according to material properties
- Use canned cycles for consistent machining operations
2. Tool Selection and Maintenance
You should select tools that are suitable for the material and machining operation, and ensure they are properly maintained. Regularly inspecting and replacing worn or damaged tools can significantly reduce the occurrence of tool marks.
3. Machine Setup and Stability Improvements
Ensuring that the machine is properly calibrated and that the workpiece is securely fixtured can reduce vibration and chatter, which are common causes of tool marks. You can also enhance machine stability by using rigid tooling and optimizing the machining process.
4. Post-Processing Solutions for Existing Tool Marks
For parts that already have tool marks, post-processing solutions can be employed to improve the surface finish. Techniques such as grinding, polishing, or lapping can be used to remove or mitigate tool marks. You should select the most appropriate post-processing method based on the material and the desired surface finish.
By implementing these solutions, you can significantly reduce the occurrence of tool marks on CNC machined parts and achieve a higher quality surface finish.
Conclusion
Preventing tool marks on CNC machined parts requires a proactive approach, incorporating best practices into your manufacturing process. By understanding the causes of tool marks and implementing effective solutions, you can minimize these defects and achieve high-quality surface finishes.
To prevent tool marks, focus on regular tool maintenance, optimized cutting parameters, and proper machine setup. CNCPOR has established a strict processing procedure to apply these best practices to our work. We can customize high – quality CNC parts according to your requirements. You can contact us at any time to get a quote.