Brass parts have golden color but black spots may appear on their surface when you work on them through CNC machining. This not only affects their looks but quality too. Good news is that it can be avoided or corrected if already happened. In this blog post we will guide you on why brass turns black and how to keep it in its best condition.
Brass Composition
Zinc and copper are the main constituents of brass. Different types of brass can be produced if you change the ratio of these metals. Machining brass is not easy therefore lead is also added in it. This addition is particularly important for CNC machining.
Here’s a table of typical brass composition.
| Alloy Name | Copper (Cu) | Zinc (Zn) | Lead (Pb) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Red Brass (C230) | 85% | 15% | <0.05% |
| Cartridge Brass (C260) | 70% | 30% | <0.07% |
| Free Machining Brass (C360) | ~61.5% | ~35.5% | 2.5–3.7% |
Main Properties of Brass Relevant to Machining

Anti-Corrosion
Brass is corrosion resistant particularly in moist environments. When it comes in contact with air, a patina (protective layer) forms on the surface. This layer stops the rust you’d normally seen on iron.
Looks
Brass stands out for its golden color and classic look. If you polish it, it will bring out a modern shine but if you let it age then it creates a vintage patina on its own. Because of this extraordinary quality it is broadly used in architectural and other decorative works.
Machinability
Machining brass is simple and easy and also saves production cost and time. Different grades like C36000 are known for their outstanding machinability. These grades let you work on them at high speed and tools also last longer. Therefore manufacturers can produce detailed brass parts with smooth finish.
Why Brass Parts Go Black
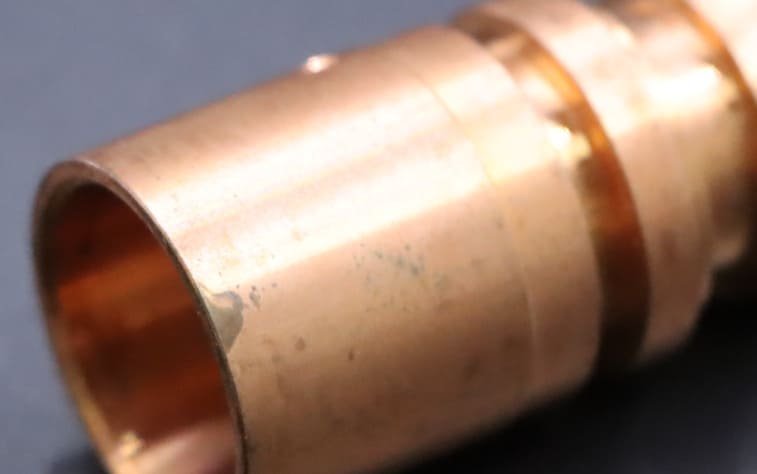

Machining Induced Oxidation
Brass can turn black because of oxidation (when it comes in contact with oxygen).
Atmospheric Exposure
Brass surfaces exposed during or after machining react with moisture and oxygen in the atmosphere. It’s a natural process and forms black copper oxide. Humid conditions increase the speed of this process because moisture increases the corrosion rate.
Heat during Cutting
When cutting tools come in contact with brass they generate a lot of heat. Their temperature can reach between 400°F and 600°F. This level of heat increases the chances of oxidation which results in darkening of surface.
At RICHCONN our engineers adjust cutting speeds & tool paths carefully. This keeps brass parts bright and minimizes overheating.
Surface Changes After Cutting
Heat from Surface Polishing
Although polishing improves the surface finish quality but it also produces heat. As a result the surface gets hot and any leftover contaminants or oils can oxidize. This oxidation then causes black spots.
Atmospheric Reaction
Brass surfaces can react with salts, dust or airborne pollutants. These substances stick to the metal and in moist environments start to corrode it. As a result green or black deposits may form.
Problems with Cutting Fluids
Poor Cleaning
If parts are not cleaned in a proper way then leftover fluids or agents stay on the brass surface. These fluids can cause contamination or may react with the metal which results in blackening and stains with the passage of time.
Fluid Breakdown
Coolants can collect stray oils, metal particles and bacteria over time. These impurities can break down the fluid or change its chemical structure. Therefore it can stain the brass or leave black spots.
How to Prevent Brass Parts from Blackening

Optimization of Machining Parameters
Use of Right Cutting Tools
Choice of right cutting tools is very important to avoid damage and excessive wear. Use sharp tools when machining brass. For this purpose carbide blades work well and a positive rake angle reduces both tool wear and burr formation.
Cutting Speeds & Feeds Control
Controlling cutting speeds and feeds is key. Brass being a soft metal benefits from slower feeds and speeds. This feed and speed control also controls chip formation which protects the machine. Moreover minimizing these values reduces heat which is the main cause of oxidation.
Coolant Management
In-time Replacement of Cutting Fluids
Cutting fluids lose their effectiveness over time. You should change the coolant after every 6 or 12 months. If it smells bad or you detect some contaminating agents in it then replace it as soon as possible.
Also keep an eye on pH level and concentration of coolant regularly. Its pH should be between 8.5 to 9.5 and concentration between 5% & 10%. This will save your coolant from bacterial growth and give outstanding performance.
Proper Cleaning
Clean your parts right after machining. This will clear leftover oils, cutting fluids and other contaminants; because if they stay, they can react with brass and cause blackening.
At CNCPOR, each part is ultrasonically cleaned and rinsed with pure water before inspection and packaging.
Post-Machining Treatments
Protective Coatings’ Usage
Brass needs protection from the environment. For this purpose you can use powder coating, lacquer or metal plating like chrome or nickel. These coatings work as a shield which not only prevents corrosion but oxidation too.
Storage of Brass Parts
Finally you have to store your finished parts and for this purpose put them in an area with controlled humidity. You can also put these parts in oil for added protection. It will keep moisture and air away from your parts.
How to Fix Already Blackened Brass

Restoring Original Look
Clean with a Suitable Cleaning Agents
Gentle cleaning of the surface is important and it is mostly done using water and some cleaning agents. If you see a minor tarnish on the surface then wash the part with warm water and mild soap to remove this surface dirt.
For easy removal you can also mix salt and vinegar in equal amounts to form a paste; put this paste on the brass surface. After 10 minutes scrub it off using a soft brush and then wash it thoroughly. It helps remove oxidation, all the while avoiding harsh chemical usage. Moreover commercial brass cleaners are also available. They remove tarnish effectively and won’t harm the metal.
Manual Polishing
Next step is shining the surface to enhance its look. For this purpose manually buff the brass with a soft cloth in order to get a simple finish. Moreover if you need a smooth and polished surface then you can also use a buffing wheel. Always polish softly to avoid scratching.
Chemical Treatment
Oxide Removers
Chemical oxide removers are used for those brass parts which have severe blackening. These removers are mostly acidic solutions like diluted HCl (Hydrochloric acid) and they dissolve the oxide layer of copper. You have to follow all safety guidelines when using these chemicals.
Surface Passivation
Now if you want to protect brass from future blackening then use passivation. For this purpose you have to submerge the part in a passivation solution (such as a copper salt mixture). This process forms a layer on the surface of brass at room temperature. This layer resists oxidation and your brass will not turn black again.
Final Protective Steps
Protective Coatings
A new coating is applied in the end and for this purpose you can use wax or lacquer. It will stop moisture and air to pass through. You can also go with powder coating as it works well and provides strong, long term protection.
Store It Right
Now you have to store these parts as a final step and for this purpose put them in low humidity (moisture‐less) areas to minimize contact with elements that can cause tarnishing.
CNCPOR has advanced packaging and climate controlled storage so your brass parts stay looking new and arrive perfect.
Conclusion
Brass parts can blacken because of different reasons like poor handling, some kind of surface reactions or oxidation. You can still maintain the durability and appearance of brass with the help of proper machining parameters, using protective coatings and through regular cleaning. For professional CNC brass machining services you can contact us anytime.
Related Questions
Does machining speed affect discoloration of brass parts?
Yes. Higher machining speeds generate heat. More heat accelerates oxidation or triggers reactions with lubricants which can cause blackening or discoloration on brass parts.
Does humidity have any effect on brass blackening during CNC machining?
Yes humidity (moisture) from the air allows oxidation which tarnishes brass. If machining is done in a humid environment then oxidation process happens faster and parts can blacken sooner.
Does brass’s blackening depend on type of alloy used in CNC machining?
Yes the alloy you choose matters as alloys differ in their corrosion resistance. Some are more sensitive towards blackening or discoloration when machined.
Can brass parts blacken if not stored properly?
Yes. Storing brass in dirty, humid or chemically reactive places allows grease breakdown and surface oxidation. These conditions will gradually turn brass parts black.
Can a cutting fluid make brass parts blacken?
Yes. If you use a wrong cutting fluid which is incompatible with the surface; it can react chemically with the brass and discolor it.